For many of us, summer is the most beautiful time. But beware of the sun! Here you can find out how you can prevent an allergy to the sun.
Preventing sun allergy: Introduction
The sun allergy is not an allergy in the strict sense. It describes various complaints that are triggered in some people by contact with the sun.
One common feature is the body’s non-functioning protective mechanism against UV radiation. You can find out here which symptoms result from this, how you can increase your sun protection and thus minimize the risk.
Symptoms
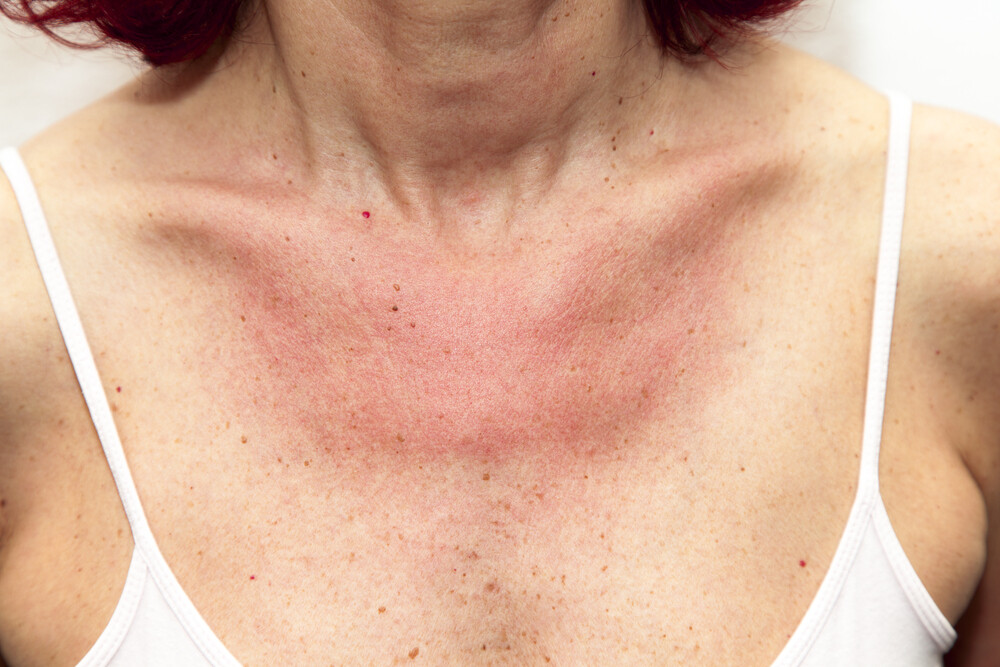
The symptoms of a sun allergy differ from one another depending on its severity. The most widespread is the so-called polymorphic light eruption (PLE), which particularly affects young, fair-skinned women. The term polymorph means versatile and refers to the complexity of potential symptoms:
- Itching
- Burning
- Skin redness
- Skin swelling
- Blisters or lumps on the skin
In particular, the areas that often come into contact with the sun and thus with the sun’s rays in summer (neck, shoulders, arms, legs) are increasingly affected. The susceptibility is also particularly high in phases in which the skin comes into stronger contact with the sun again after a longer period of time, for example in spring.
Other known forms
- Mallorca acne: As funny as the name sounds, Mallorca acne is a special form of PLD. It resembles acne in appearance and also occurs more frequently in people who are prone to acne.
- Phototoxic reaction: Due to chemical substances, the skin becomes more sensitive to sunlight and is more prone to sunburn. The skin itches, hurts or discolours. The reaction can be triggered by contact with perfumes or special plants.
- Photoallergic reaction: This form is actually an allergy. The body develops antibodies against drugs or make-up, for example, so that the skin triggers an allergic reaction the next time it comes into contact with the substance and sun rays.
Preventing sun allergy: 4 practical tips
- Sunscreen: Sunscreen is an important factor when it comes to sunscreen products. It is important that you apply sunscreen 30 minutes before going out into the sun and that you reapply it after each bath in the water. The sun protection factor should be at least 30, ideally 50. Prefer sunscreens that are free of fats and emulsifiers.
- Solarium: If you are prone to a sun allergy, you can slowly get used to the sun by visiting a solarium. However, you should not overdo it. A few minutes are enough and, depending on your skin type, you should consult your dermatologist in advance. Make sure that both UVA and UVB rays are used, as the polymorphic light dermatosis can only be triggered by both.
- Phototherapy: At the dermatologist you can do a light hardening by phototherapy. In phototherapy, the skin is irradiated with UV light several weeks before a sunny holiday.
- Micronutrients: Especially calcium, beta-carotene and some vitamins are considered to be effective micronutrients for the prevention of sun allergy. However, this has not been scientifically proven and you should consult your doctor about which preparations are useful for you.