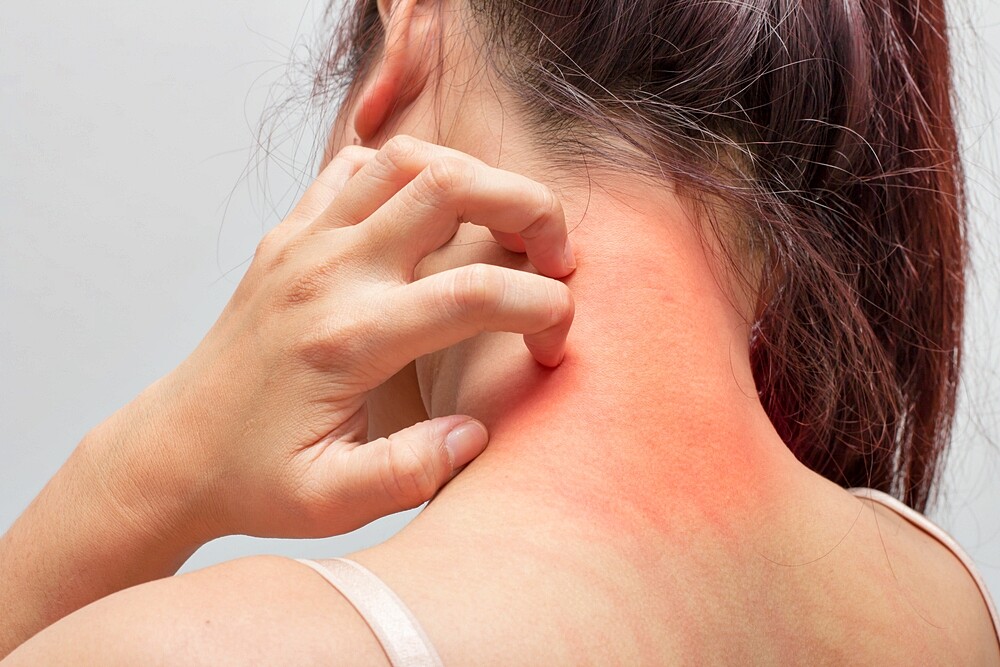
Itchy skin is an indication that the balance of the skin is disturbed. The need to scratch is now great – but this would not be a good idea. What helps against itching and how we can calm our skin again.
Itchy skin can torture us, because itching (medical term “pruritus”) and scratching are a fatal combination
Itching occurs as a reaction of the immune cells to a stimulus from inside or outside. The signal to the brain is then called: Scratch! Unfortunately for our skin this is rather the wrong measure, because scratching is now rather counterproductive. It is not a therapeutic measure as it does not eliminate the causes of the skin itching. A vicious circle develops: Constant scratching further irritates dry, itchy skin. The body releases inflammatory messengers such as histamine, which further intensifies the itching. In addition, we can injure our skin when scratching. If bacteria get into the skin surface, the wound becomes inflamed. It is important to clarify why the skin itches and what we can do about it.
Itchy skin: Contagious or harmless?
If the skin itches, let’s start with the cause: Are chronic skin diseases such as psoriasis, neurodermatitis or contagious ones such as scabies (which has become more common again in our country for some time), chickenpox, rubella, a skin fungus or hives (urticaria) the cause of itching? Diabetes can also be a reason for extremely dry skin. This must be clarified quickly in order to find a therapy – depending on the cause – or even to avoid a possible infection. If pustules and inflammations are added or the itching spreads over a large area, the family doctor or dermatologist can make the right diagnosis. Often, however, the itching is caused by very dry skin.
According to a study of the University of Münster, about 12 percent of the younger population up to 30 years and about 20 percent of the older population between 61 and 70 years suffer from chronically itchy skin. More than 90 percent do not take any treatment.
Skin care for itchy skin
- The facial skin not only lacks fat, but also moisture. Pay attention to moisture-binding ingredients in face creams: Urea, hyaluronic acid, dexpanthenol (also has anti-inflammatory and wound healing properties), niacin vitamin B3 (improves the barrier function of the skin and stimulates the production of the skin’s own fats).
- Perfumed skin care products with preservatives (parabens) and mineral oils (Paraffinum Liquidum – here we explain why cosmetics should do without mineral oils) should be avoided. Especially skin care products from the pharmacy are aimed at itchy skin. Some products help with linoleic acid, silver ions, Dead Sea salt, plant extracts of horsetail, willow herb, calendula and camomile.
- SOS-Cosmetics: Intensive ointments or acute sprays can usually soothe severe itching quickly.
- In summer, the skin usually needs less oil than in winter – so switch to richer textures in autumn. We explain which ingredients should be included in face creams for dry skin.
- Work with oils when cleansing the face: Micellar water or facial tonic sometimes dry out the skin, cleansing oils or face milk are better.
- Instead of perfumed shower gels, it is better to use a neutral shower oil.
- Do not shower too hot, this dries out the skin. Long, hot baths stress the protective mantle of the skin.
Home remedies for itchy skin
- Zinc ointment can help with small skin areas, larger areas can be treated in the bathtub: A bath in black tea or horsetail tea helps with tanning agents against itching.
- Envelopes with vinegar water (one tablespoon of vinegar to one litre of water) or oak bark stock.
- Cold Aloe Vera Gel (from the refrigerator) – it should be one hundred percent natural
- Olive oil and honey as a mask can quickly soothe the skin.
- A study by the Dermatology Department of the National Research Center, Cairo University, has shown that peppermint oil also helps against itching. Always apply diluted (for example in almond oil), it can directly irritate the skin.
What else can help with itchy skin?
- Physical stimuli such as pressure, rubbing, rubbing and scratching of clothes can provoke itching. Loose fitting garments made of natural fibres are best for the skin.
- Organic is better: many clothes contain chemicals, and the parts produced in low-wage countries contain textile auxiliaries and dyes to which our skin can react strongly. Therefore, the following applies anyway: Always wash new clothes before wearing them! Sustainably produced clothing does not use any harmful chemicals.
- Use fragrance-free detergents and avoid using perfumed fabric softeners
- Be cool: Cooling with packs can sometimes help to suppress the intense itching: The cold receptors in the skin lie on the itchy nerves. If they are activated, this leads to suppression of the itching signals.
- Remove hot spices from your diet – they make us sweat and this can also dry out the skin. Anything that stimulates the blood circulation of the skin usually leads to more itching.
- Alcohol and nicotine should now be taboo.
Itchy scalp: What helps
It is not always lice that cause itchy scalps. The scalp can dry out quite a bit if we maltreat it daily with fragrant shampoos in overdosed amounts and add perfumed conditioners and hair masks. Soothing shampoos with willow bark, evening primrose or urea. It is better to avoid anti-dandruff shampoos or shampoo for greasy hair more often. A soothing neem oil treatment can help against itching on the head. Also: Do not blow-dry your hair too hot and do not apply styling products to the scalp.
The skin becomes drier and slower
It is mean: unfortunately, our skin gets lazy with age. It no longer produces as much hyaluronic acid and collagen, the skin becomes drier and no longer looks as firm. The activity of the skin glands also decreases: The sebaceous glands produce less sebum, the sweat glands produce less sweat. This often results in dry itchy skin. Our beauty routine should be adapted to our skin condition. However, not every anti-aging product is suitable for dry and itchy skin. Creams with high doses of retinol (vitamin A) – in the USA concentrates of up to one percent are allowed, in Germany only up to 0.5 percent – can irritate and dry out the skin. Retinol in a very low dose (less than 0.1%), combined with moisturizing active ingredients, does not harm mature skin.
In winter the skin itches more often
We have often heard that the heating air is to blame. Low humidity, as is the case in overheated or air-conditioned rooms or in cold winter weather, dries out the skin. So now it’s time for more intensive care and to incorporate more fat than moisture into the skin care routine. Evening primrose, almond and macadamia oil can be integrated drop by drop into your favourite skin care routine. Special products like winter creams help the skin to balance cold and dry air. Especially rough areas should be creamed several times a day (make sure that the care product does not contain mineral oil – this has a counterproductive effect as it forms a film on the skin which prevents the exchange of moisture and thus dries the skin surface even more).
Does the psyche also play a role?
As always, the answer is yes. People with stressful life events suffer from itching more often (12.2 percent) than people with many friends. A study from Münster shows that the psyche plays a role in pruritus: Around 70 percent of the patients also suffered from psychosomatic or psychiatric illnesses.
Take it easy
Meditation, yoga, breathing techniques that calm us down – and the power of positive thoughts: this also helps with skin diseases. Our dermis in particular interacts strongly with our psyche (the skin is known to be the mirror of the soul …). Music can also help us to find some relaxation. According to studies, this anti-stress song has been proven to help us find peace. If you can’t resist the itching, you can grab a scratch pad (a car sponge covered with chamois leather will also do). This can also help children who suffer from neurodermatitis. It’s also good to do some relaxation exercises in the evening so that the itching doesn’t rob us of sleep.