Hyposensitization is used to treat allergies such as hay fever. We explain exactly how the procedure works and whether it helps.
What is hyposensitization?
Hyposensitization is intended to reduce the symptoms of allergies or at best to prevent them completely. The basic idea behind the therapy is that the body gradually becomes accustomed to the allergen (e.g. pollen in hay fever) so that it no longer reacts to it. During the procedure, the skin is repeatedly exposed to the allergen. The dose is gradually increased. In colloquial language, hyposensitization is also known as “allergy vaccination“.
Why is hyposensitization useful?
Unlike, for example, treatment with medication, which only alleviates hay fever symptoms or the symptoms of other allergies (e.g. insect venom allergy or house dust allergy), hyposensitization is the only method that addresses the cause of the symptoms: Hypersensitivity to an allergen. Although the allergy as such cannot be eliminated by hyposensitization, the probability of allergic reactions is minimized. With fewer allergy symptoms, the lives of those affected are significantly improved – even if there is a cross-allergy.
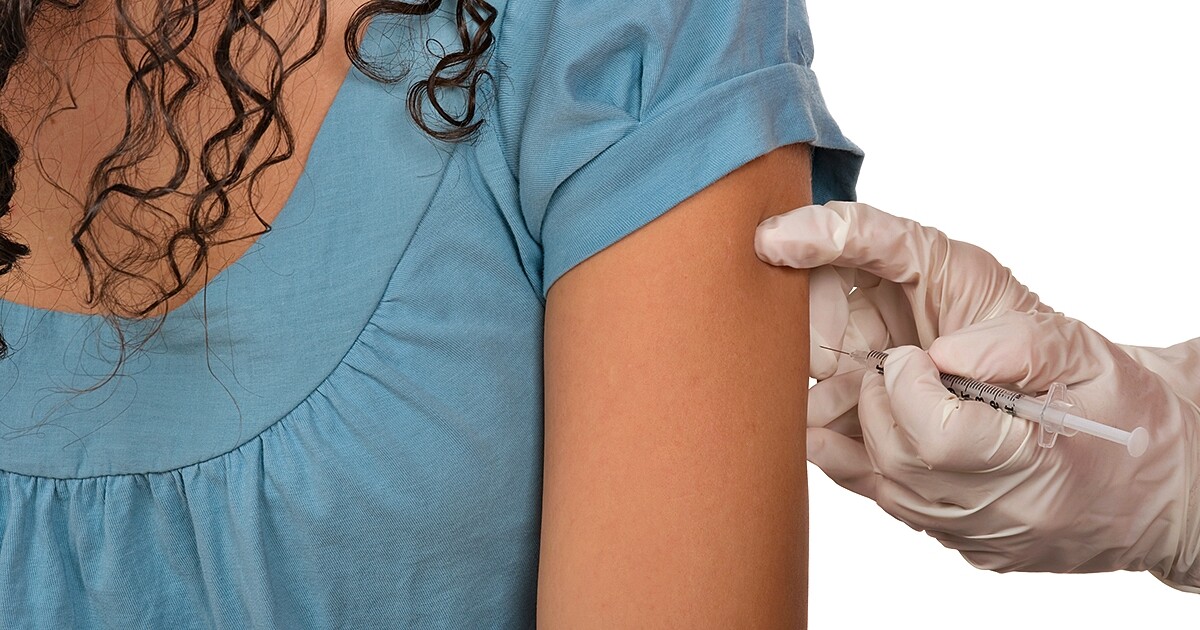
How does the hyposensitization process work?
As much as hyposensitization can bring – patients must have a lot of patience for the treatment. In the initial treatment (intensification phase), the allergen extract is injected under the skin weekly. This is also called subcutaneous treatment. The administered dose is increased every week up to a defined maximum amount. Provided that no side effects occur, one can switch from the increase phase to the so-called maintenance therapy. In this phase, the doctor injects the maximum amount of solution once a month.
The procedure usually lasts for three years. However, there is also a so-called short-term therapy (pre-seasonal immunotherapy). Here, treatment is only given in the time before the pollen season – with at least three repetitions, which means that this procedure also takes three years. The insect venom allergy has a special position: the hyposensitization against this allergy takes five years instead of three.
By the way: there is another form of hyposensitization. In sublingual immunotherapy, the allergen is placed daily under the tongue by the patient in the form of a drop or tablet and swallowed after a while. However, this form of hyposensitization is not suitable for every allergy.
For whom is hyposensitization suitable?
Not all allergy sufferers can carry out hyposensitization. The therapy is useful if:
- it has been proven that the complaints come from a specific allergy,
- the allergen is unavoidable in everyday life (e.g. by spreading too much),
- strong symptoms occur, which are hardly improved by other treatments,
- the patient is older than five years.
House dust allergy, neurodermatitis, latex allergy etc.: When should I not undergo the treatment?
Conversely, there are also cases in which the therapy cannot be applied. These include:
- Asthma that cannot be controlled enough despite treatment
- Severe cardiovascular, current cancer and autoimmune diseases
- Treatment with beta blockers
- Pregnancy
- Nickel allergy
The doctor can make an individual decision as to whether hyposensitization is appropriate. This also applies if there are cross-allergies.