An ectopic pregnancy is difficult to detect and can suddenly become life-threatening. You can recognize them by this…
What is an ectopic pregnancy?
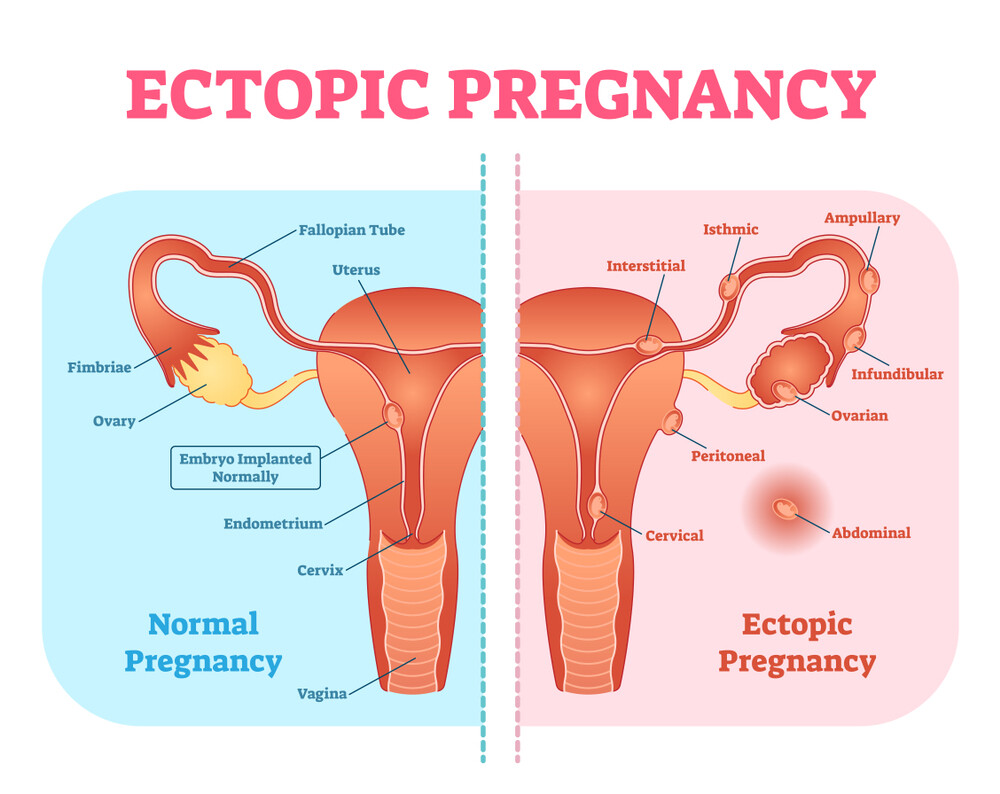
Doctors speak of an ectopic pregnancy or tubal pregnancy if the fertilised egg (zygote) does not settle in the wall of the uterus but in the fallopian tube. This happens, according to statistics, in one in 150 pregnancies. Normally, the ovum travels through the fallopian tube for 5 days and then starts to implant on the sixth day. Reasons why this does not take place in the uterus can be adhesions and adhesions of the fallopian tube (e.g. endometriosis) or so-called functional disorders.
Just like a pregnancy in the abdominal cavity, ovary or cervix, ectopic pregnancies are also called extrauterine pregnancies or extrauterine or ectopic pregnancies. In these pregnancies, the zygote nests outside the uterus (ectopic and extrauterine = outside the uterus). This often goes unnoticed at first.
How is a so-called tubal pregnancy recognised?
In order to exclude diseases with similar symptoms, some tests must be carried out. The patient is also palpated externally and internally on the lower abdomen and ultrasound examinations are performed. During the imaging examinations a healthy pregnancy in the uterus can be determined. An early ectopic pregnancy and the still small embryo on the other hand are very difficult to see in the tubes (fallopian tubes).
Have the pregnancy hormone HCG checked regularly!
Of course it must be determined whether the patient is pregnant. Pregnancy tests are carried out with urine and by taking blood samples. If the pregnancy is intact, the pregnancy hormone HCG increases very quickly. Therefore, if there is uncertainty about the type of pregnancy, long-term observation of the HCG concentration in the blood serum is necessary. A pregnancy that is not intact or ectopic is also conspicuous by a barely rising or even suddenly falling HCG level.
A detailed anamnesis (looking at the medical history) is necessary to identify given risk factors for ectopic pregnancy. These can be operations in the abdomen, as well as previous misalignments, diseases or adhesions.
These are possible symptoms of ectopic pregnancy
- Positive pregnancy test
- Pulling or pricking in the lower abdomen, if necessary
- Pain
- One-way
- Nausea
- Swindle
- Breast Tensions
- Bleeding (but no period)
Often unnoticed at first
At the beginning of this form of ectopic pregnancy, the embryo develops normally in the fallopian tube. However, ectopic pregnancies usually end before the end of the third month of pregnancy, due to lack of space and insufficient supply. This leads to the discharge with bleeding.
An ectopic pregnancy can quickly become life-threatening!
Therefore always consult a doctor or clinic if you suspect that you are pregnant. Listen to the symptoms and do not ignore pain and bleeding. If the fallopian tube ruptures, there is a risk of life-threatening bleeding into the abdominal cavity. If in doubt, a laparoscopy must be performed immediately.